Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the healthcare sector, especially in medical diagnosis. Through the use of sophisticated algorithms, AI supports healthcare providers in making quicker, more precise decisions, ultimately resulting in better patient outcomes.
With its capacity to process large volumes of medical data quickly, AI improves disease detection, patient monitoring, and treatment planning. This article discusses how AI is transforming medical diagnosis, its major applications, advantages, disadvantages, and future prospects.
What is AI in Medical Diagnosis?
- Definition and Objective: AI-based medical diagnosis employs machine learning and deep learning technologies to process and interpret complex medical information, help detect diseases, monitor them, and develop tailored treatment plans. The objective is to improve diagnosis accuracy, eliminate human errors, and optimize clinical processes.
- How It Works: AI models are trained on large medical datasets, such as medical images, electronic health records, and genetic data. Through pattern and correlation identification, AI systems generate accurate diagnostic recommendations that augment human intelligence.
- Example: In radiology, AI can examine mammograms to identify early indicators of breast cancer more accurately than human radiologists.
Why AI in Medical Diagnosis is Important
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
- Pattern recognition is performed by AI algorithms, reducing misdiagnoses and false positives.
- In radiology, abnormalities such as tumors, fractures, and neurological diseases are diagnosed with accuracy even in difficult-to-decipher medical images.
“AI is the stethoscope of the 21st century.” – Eric Topol, Scripps Research.
2. Early Detection and Timely Intervention
- AI identifies diseases at earlier stages, allowing timely interventions that enhance patient survival rates significantly.
- For example, AI-based tools can detect diabetic retinopathy in retinal scans, enabling early treatment and avoiding vision loss.
3. Personalized Medicine and Treatment Plans
- AI processes patient-specific information, such as genetic, lifestyle, and medical history, to provide personalized treatment plans.
- In cancer care, AI prescribes cancer treatment based on the genetics of tumors and the patients’ responses to past treatments.
- This tailored method optimizes the effectiveness of treatments and reduces adverse effects.
4. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- AI takes over monotonous administrative tasks, leaving healthcare professionals to work less.
- AI chatbots address patient queries, make appointment bookings, and give initial diagnoses, freeing up clinicians to tackle difficult cases.
- AI systems also optimize clinical processes by effectively screening electronic health records.
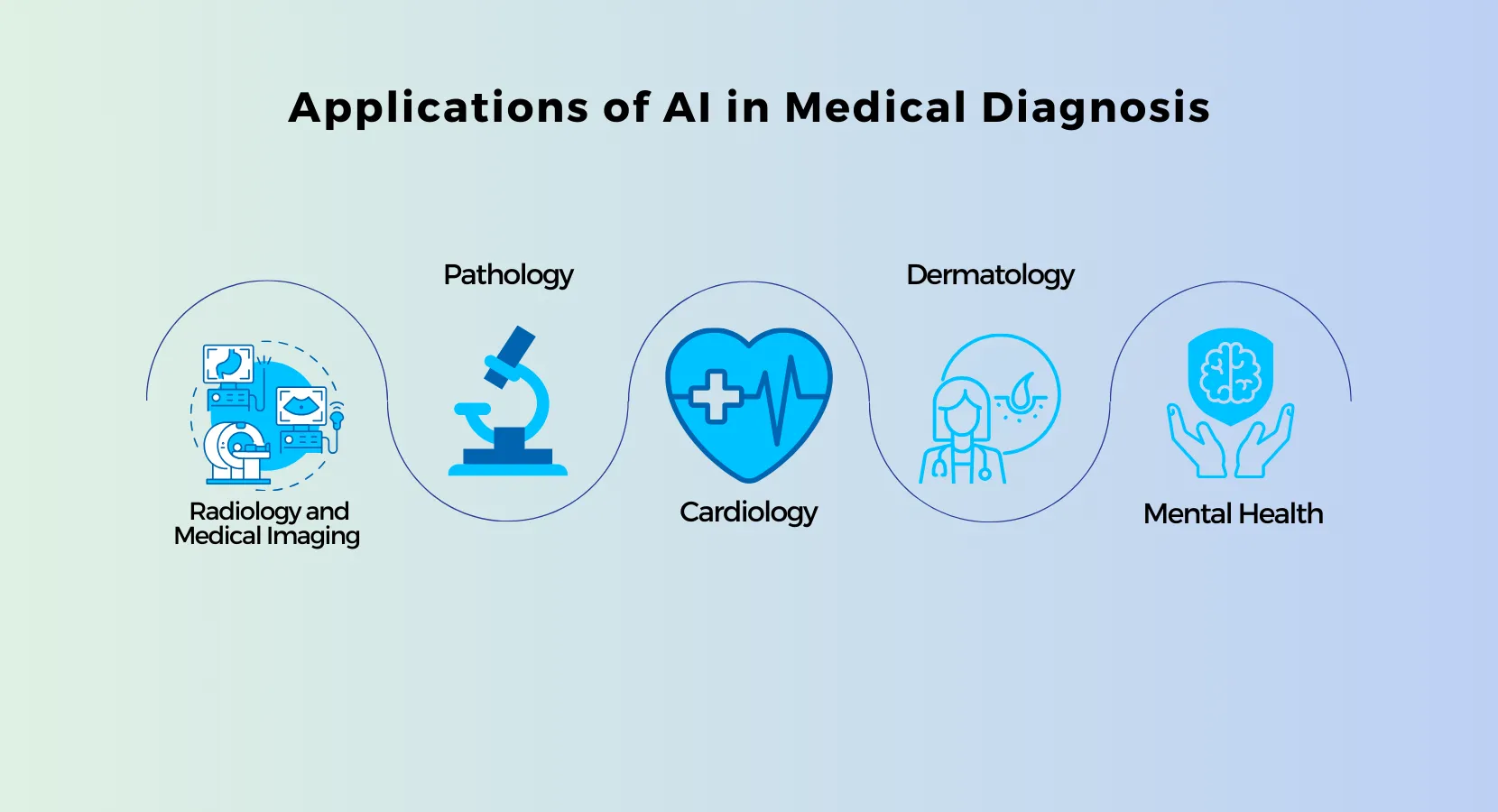
Key Applications of AI in Medical Diagnosis
1. Radiology and Medical Imaging
- Enhanced Image Analysis: AI greatly enhances image analysis to enable radiologists to identify fractures, tumors, and neurological disorders more accurately.
- Faster Diagnoses: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans are processed quickly by advanced algorithms compared to standard techniques, which allows for swifter and more accurate diagnoses.
- Example: An AI model to identify eye disease from retinal scans was built by Google’s DeepMind and performed as well as expert eye doctors, indicating the potential for AI in optimizing medical imaging.
2. Pathology
- Artificially intelligent microscopes scan tissue samples, detecting cancer cells with precision.
- This tech speeds up diagnostics, minimizes human error, and enhances diagnostic accuracy.
- Example: Paige AI employs deep learning algorithms to diagnose prostate cancer in biopsy samples with high accuracy.
3. Cardiology
- AI models examine electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms to identify heart abnormalities.
- These systems detect precursors of cardiovascular diseases, which allow early intervention and individualized treatment strategies.
- Example: AliveCor’s KardiaMobile detects atrial fibrillation, a top cause of stroke, using AI through ECG testing.
4. Dermatology
- Artificial intelligence systems diagnose dermatological conditions through evaluation of high-resolution images of moles, rashes, and lesions.
- They precisely identify benign and malignant dermatological conditions with fewer unnecessary biopsies.
- Example: Google Health’s DermAssist applies AI to offer dermatological diagnoses, instructing users to consult a doctor when necessary.
5. Mental Health
- AI solutions track patient speech and behavior patterns, identifying initial signs of mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
- These applications aid in remote patient monitoring and customized mental health interventions.
- Example: Woebot, an AI chatbot, offers cognitive behavioral therapy and mental health guidance through live chats.
Real-World Success Stories
- IBM Watson Health partnered with top cancer centers to create AI solutions that suggest cancer treatment plans based on patient information and medical literature.
- PathAI collaborates with pharma companies to enhance diagnostic accuracy in pathology for better drug development and personalized medicine.
- Aidoc applies artificial intelligence to review medical images in real time, helping radiologists prioritize severe cases for quicker diagnosis and treatment.
Business Opportunities in AI Medical Diagnosis
1. AI-Driven Diagnostic Solutions
- Startups can create AI-based diagnostic solutions for hospitals, clinics, and telemedicine platforms.
- There are opportunities in developing specialized AI models for radiology, pathology, cardiology, and dermatology.
2. Medical Imaging Software and Platforms
- AI-based imaging software can be licensed to medical institutions, making diagnostic workflows more efficient and accurate.
- Cloud-based AI platforms for medical imaging provide scalable solutions for remote diagnostics.
3. Healthcare Data Analytics
- AI-based healthcare data analytics yield actionable insights for population health management and personalized medicine.
- Firms can provide predictive analytics solutions for preventive care and early disease detection.
4. Integration with Telemedicine
- Telemedicine platforms integrated with AI-powered diagnostic tools improve remote patient monitoring and consultations.
- This model increases access to healthcare, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
5. AI Training and Consulting
- With increasing adoption of AI, there is a need to train healthcare professionals to utilize AI diagnostic tools effectively.
- Healthcare providers can be assisted by consulting services in implementing AI solutions while maintaining regulatory compliance and data security.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Data Privacy and Security
- Artificial intelligence models handle sensitive patient data, putting a spotlight on data security and privacy.
- Data compliance with medical regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR is significant in building confidence in patients’ data protection.
2. Bias and Fairness
- There is a likelihood that AI systems will pick up biases from datasets, causing disparity in diagnosis efficacy between various populations.
- It is imperative to achieve diverse and generalizable training datasets to mitigate biases and enhance fairness.
3. Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
- Regulatory mechanisms must evolve to monitor AI deployments in healthcare while ensuring safety and ethical usage.
- Ethical implications, including AI decision-making transparency and accountability, must be taken into consideration.
4. Integration and Adoption
- Successful integration of AI systems involves the need for specialized training of healthcare professionals.
- Adoption is usually thwarted by resistance to change, the cost of implementation, and fear of AI taking away human jobs.
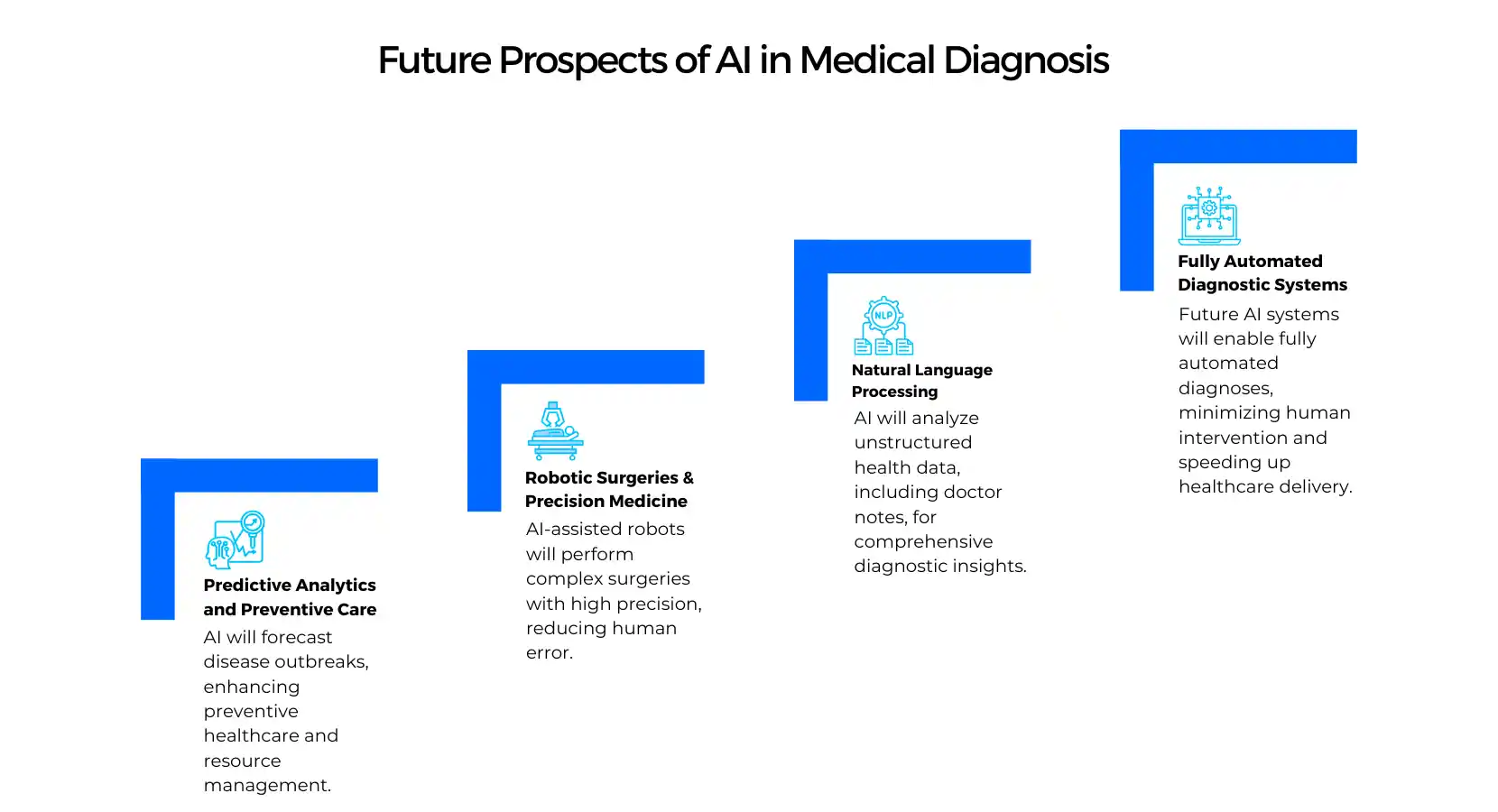
Future Prospects of AI in Medical Diagnosis
- Predictive Analytics and Preventive Care: AI will forecast disease epidemics, which will facilitate preventive healthcare and optimizing resources.
- Robotic Surgeries and Precision Medicine: Robotic systems that are aided by AI will likely carry out complicated surgeries with utmost precision, eliminating human errors.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Artificial intelligence models will scan unstructured health data, including physician notes, to give holistic diagnostic insights.
- Fully Automated Diagnostic Systems: The future AI systems can provide fully automated diagnoses with less human interaction and faster healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
AI in clinical diagnosis is transforming healthcare by increasing diagnostic precision, facilitating individualized treatment regimens, and streamlining operational effectiveness. As AI technology continues to advance, its application in medical diagnostics will be increasingly invaluable, leading to a healthier future. Adopting these innovations will allow healthcare professionals to provide improved care, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes globally.
This piece illustrates how AI-based medical diagnosis is revolutionizing the healthcare sector through increased precision, efficiency, and customized patient care. Its capability to change the way disease is detected, treatment is planned, and the patient is monitored represents a paradigm shift towards enhanced healthcare delivery.