Table of Contents
High-hazard industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, mining, and aviation have long faced the challenge of minimizing risk while maintaining efficiency. Failure in these sectors can have devastating consequences, from environmental damage to threats to human life. In recent years, artificial intelligence has emerged as a powerful tool for identifying vulnerabilities and helping organizations respond faster and smarter.
This article talks about how this technology is helping improve risk management across several industries.
From Reactive to Predictive: A Shift in Approach
Traditional risk management models rely heavily on historical data, incident reports, and human judgment. While these methods have served a purpose, they miss patterns hidden deep in datasets or overlook the early signals of a failure. AI offers a way to process vast amounts of data in real time. This makes detecting subtle changes that may suggest a brewing issue possible.
This shift is particularly significant in environments with chemicals or hazardous materials. Consider the example of aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF), which effectively suppresses oil-based fires. According to TorHoerman Law, AFFF contains per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Long-term exposure to AFFF has developed kidney, liver, breast, and various other cancers in firefighters and military personnel.
Moreover, AFFF ingredients are also known to cause environmental contamination. Long-term exposure risks and environmental contamination have triggered legal scrutiny in many cases. People who developed health complications due to AFFF exposure have filed a firefighter foam lawsuit. These kinds of lawsuits underscore the need for companies to anticipate not just operational risks but also legal and reputational ones.
In response, companies are turning to AI systems that can analyze chemical compositions, monitor worker exposure, and even simulate potential contamination events. This helps reduce uncertainty while providing documentation that could become crucial if health claims arise years later.
Real-Time Monitoring and Decision Support
One of the most impactful uses of AI in high-risk industries is real-time monitoring. Sensors placed throughout facilities can feed continuous streams of data into AI-driven platforms. These platforms are trained to flag abnormalities like sudden pressure spikes, temperature shifts, or unplanned chemical releases.
Even a slight delay in recognizing and responding to an issue in complex systems can lead to cascading failures. Consider the example of the mining industry, where machine failure can result in severe injuries. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 40% of acute injuries in mining are categorized as caught-in or struck-by machinery.
AI’s ability to process and analyze data quickly is a game-changer. It reduces the time between detection and response, allowing teams to act before a situation escalates. For example, these tools allow operators to react within seconds instead of hours in oil refineries or offshore platforms. Some systems recommend specific actions, helping frontline teams make faster, safer decisions during high-stress situations.
Beyond emergency responses, AI systems also support routine maintenance by identifying early signs of equipment fatigue or malfunction. Over time, this kind of predictive insight can reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of expensive machinery. It combines short-term responsiveness and long-term planning, both critical for industries where every second counts.
Strengthening Worker Safety Protocols
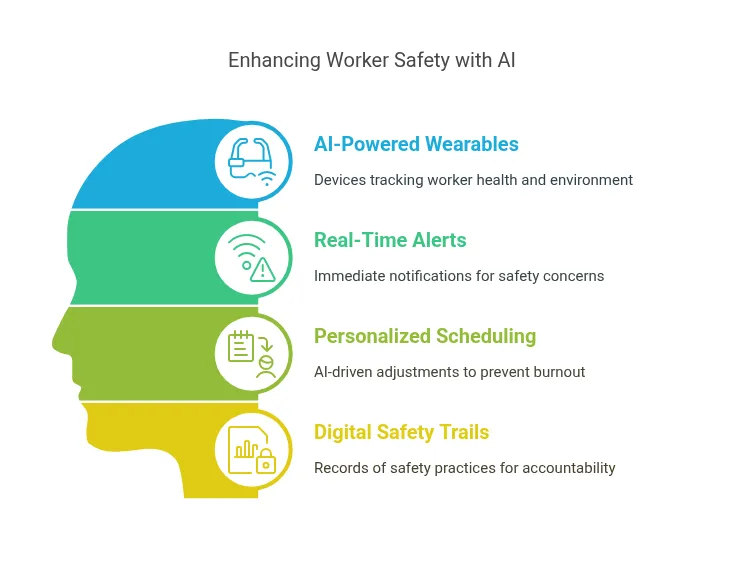
AI-powered wearables are also becoming more common in industrial settings. These devices track fatigue levels, posture, environmental conditions, and exposure to harmful substances. The collected data isn’t just used for immediate alerts but is analyzed over time to improve protocols and training programs.
These days, worker safety is more than just wearing a helmet and a harness. With AI, safety becomes a continuous process supported by real-time insights. If a worker’s posture suggests fatigue or if the air quality suddenly shifts, alerts can be sent instantly to supervisors or safety officers. This helps reduce accidents caused by delayed reactions or missed warning signs.
Some companies are also integrating AI with workforce scheduling to prevent burnout. By analyzing performance and health data, these systems can suggest break times, workload adjustments, or even reassign tasks based on an individual’s current condition. This level of personalization was nearly impossible before the introduction of AI in these settings.
In industries with a history of exposure-related illnesses, having a clear digital trail of safety practices can offer both protection and accountability. It’s a shift toward prevention rather than reaction, and it’s changing how organizations think about their duty of care.
Environmental Risk and Regulatory Compliance
From emissions tracking to water quality monitoring, AI tools help companies stay compliant with increasingly strict regulations. These tools can help monitor environmental pollution in real time and raise flags for early intervention by companies. Besides flagging problems, they often offer solutions, simulating what-if scenarios that show the outcome of specific actions.
Environmental impact is no longer a topic that companies can afford to ignore or treat reactively. With increased public scrutiny and tighter policies across global markets, organizations must demonstrate that they’re doing more than the bare minimum. AI helps by making environmental data more visible and actionable.
For example, a manufacturing plant can use AI to monitor the release of volatile organic compounds in real time. If emissions begin to exceed safe limits, the system can identify the source and recommend immediate steps to mitigate the issue. In some cases, it can even adjust operations automatically to prevent further damage.
These capabilities support more accurate reporting and greater transparency. AI-generated reports can provide regulators with detailed logs of how incidents were handled and how often checks were performed. This level of documentation not only supports compliance but also builds trust with local communities and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do companies ensure data privacy when using AI for risk management?
When organizations deploy AI systems in high-risk environments, they collect large volumes of data, including information about employees, equipment, and environmental conditions. To protect sensitive data, companies often use encryption, anonymization techniques, and strict access controls. Additionally, many opt for on-premise solutions or hybrid models to keep critical data from being fully cloud-based.
Are there ethical concerns with using AI in high-risk workplaces?
Yes, ethical considerations do arise, particularly around surveillance, worker autonomy, and data usage. For instance, while monitoring workers for safety can reduce accidents, it can raise concerns about over-monitoring and personal privacy. Companies must balance safety and respect individual rights, often through clear policies and employee involvement in system design.
What role does AI play in insurance and liability assessments in high-risk industries?
Insurers are increasingly relying on AI to evaluate operational risks more accurately. AI-generated insights help insurers offer more customized coverage plans based on real-time and historical risk data. For companies, this means that maintaining AI-powered safety systems can sometimes lead to better insurance rates or fewer claim disputes.
The use of AI in high-hazard industries isn’t just a tech trend. It reflects a more profound shift toward more intelligent, more adaptive risk management. While technology alone can’t eliminate every threat, it significantly reduces the window between a potential and a real issue. That difference in timing can save money, prevent disasters, and most importantly, protect lives.
Companies willing to integrate AI thoughtfully into their operations find that risk management becomes more about anticipating change. That’s not just safer; it’s smarter business.