Introduction
Table of Contents
With rapidly advancing healthcare technology, the world is eyeing a new revolution: augmented reality (AR) —a transformative force in medical training, patient treatment, and surgical procedures. This digital overlaying on real-world space revolutionizes how healthcare professionals approach their environment and work for better patient outcomes.
The latest research indicates that the global AR in the healthcare market has a projected CAGR growth of 30.5% until 2027, which is expected to reach $6.7 billion. These trends in growth relate to the adoption of AR technologies to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and engagement of healthcare delivery. [Source: Research and Markets, Statista]. Increased adoption of AR enhances efficiency, accuracy, and patient engagement, all critical factors driving this growth.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality is a technology that superimposes computer-generated images, sounds, or other sensory inputs onto the real world. Unlike the virtual reality system that creates a completely immersive environment, AR enhances the existing environment by adding something digital to the same. This can be experienced through all sorts of devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, so that the user views and interacts with digital content in real time, spread seamlessly over his or her physical surroundings.
How AR is Impacting Healthcare
AR is making significant strides in various healthcare applications. From enhancing surgical precision to improving medical training, the technology is reshaping how healthcare professionals deliver care and interact with patients. For instance, AR-enabled surgical navigation systems assist surgeons by providing real-time, 3D visualizations of patient anatomy during procedures, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of complications. For example, a patient experiencing chest pain can use an AR app to point to the exact location of the pain. This information can help the doctor to rule out certain conditions, such as a heart attack, and to focus on other possible causes of the pain. Some of the key impacts of AR are mentioned below:
- Surgical Procedures: AR-enabled surgical systems provide real-time 3D visualizations of a patient’s anatomy, enhancing surgical precision and reducing complication risks by up to 40%.
- Patient Engagement: With AR apps, patients can locate and visually represent pain points, giving doctors clearer diagnostics. For instance, identifying specific chest pain locations can help rule out critical conditions like a heart attack.
- Remote Collaboration: AR enables specialists to guide surgeons virtually, facilitating expert consultation in real time, especially during high-risk surgeries.
Treatment Domains Utilizing Augmented Reality
There are several treatment domains in which augmented reality and virtual reality are used to treat patients. Among those domains are:
- Pediatric Diagnostics and Treatments
- Pain Management
- Mental Health Therapy
- Neurological Disorders
- Surgery Planning & Intraoperative Procedures
- Ophthalmic Diagnostics
- Telemedicine & Virtual Care
- Post-operative and Rehabilitation Therapies
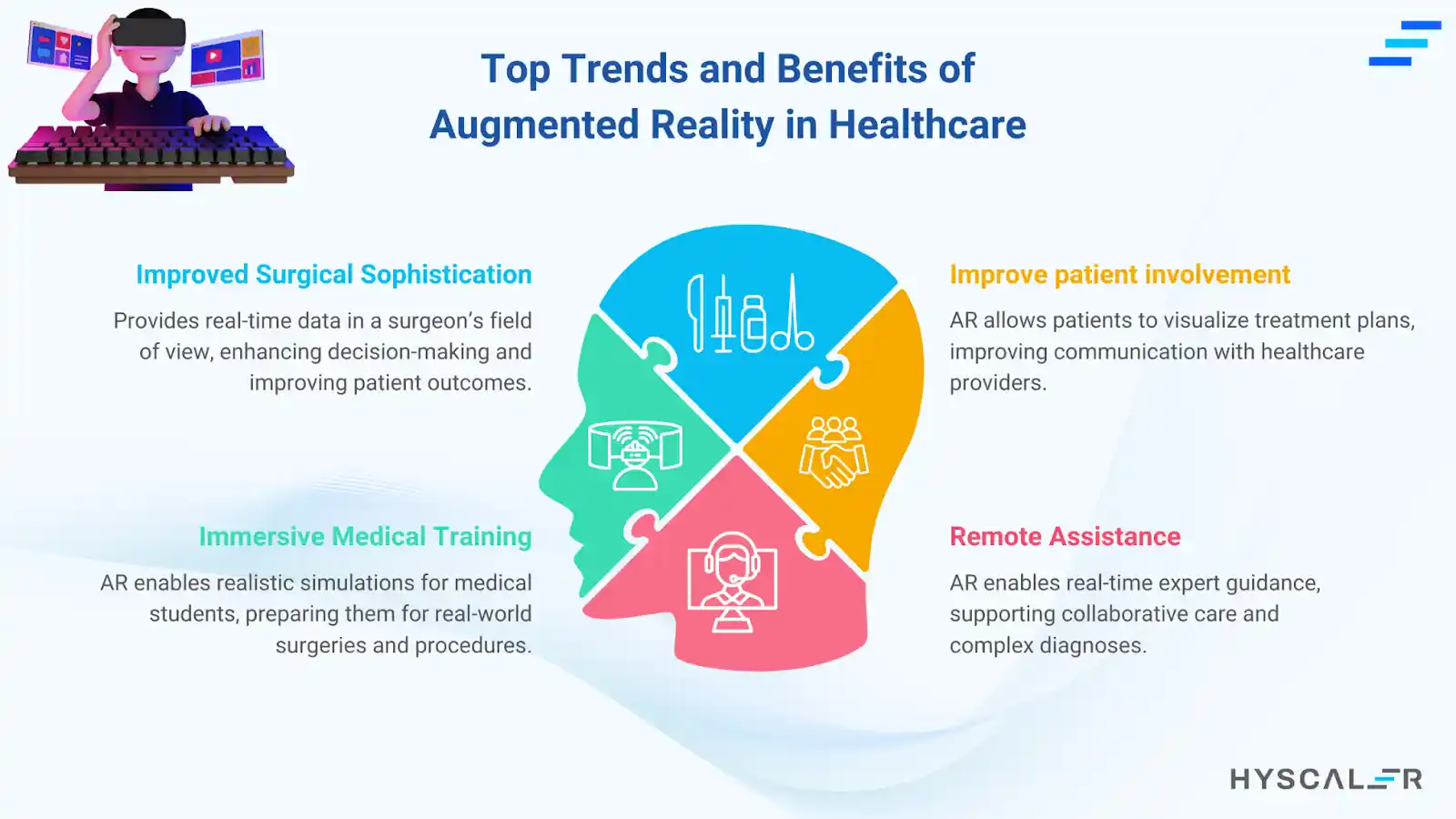
Top Trends and Benefits of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Improved Surgical Sophistication: Such information offers critical data directly in the surgeon’s line of vision during a complex procedure, improving their decision-making capabilities and ultimately leading to better patient results.
Immersive Medical Training: Medical students can be taught the realistic simulation of surgeries and procedures through augmented reality, keeping them prepared for real-world conditions while enhancing their study experience.
Enhance patient involvement: AR applications would allow patients to view treatment plans and understand procedures. It will ensure that the health providers communicate better with the patients.
Remote Assistance: AR enables experts to provide real-time expert guidance to doctors elsewhere, thus allowing for collaborative patient care and consultant help during surgeries or especially difficult diagnoses. Remote assistance prevents unnecessary patient transfers, lowering travel and hospital readmission costs.
Key Metrics That Highlight the Power of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Surgical Error Reduction Rate: AR reduces errors by up to 40%, ensuring greater patient safety.
Training Effectiveness: Retention rates among medical professionals improve by 30% when trained using AR.
Patient Satisfaction Scores: 90% of patients report high satisfaction with AR-aided treatment visualizations.
Operational Efficiency: Surgery could be cut by 20% shorter with AR. This will translate into cost savings and optimal resource usage. Healthcare Provider Adoption: The healthcare industry has rapidly adopted AR technologies. By 2025, more than 50 percent of healthcare organizations are expected to invest in AR solutions.
Adoption Rates Among Healthcare Providers: Adoption rates for AR technologies in the healthcare field are increasing rapidly, and about 50% of healthcare organizations envision deploying AR solutions by 2025.
Medical Devices Incorporating Augmented Reality
- AR Surgical Navigation Systems: These tools offer live 3D views of patient anatomy during surgery, [helping surgeons cut operational time by 20%], which translates into cost savings and optimal resource usage.
- HoloLens in Surgery: This is a Microsoft HoloLens headset that shows the patient data and anatomical structures during surgery, where it shows imaging studies in a CT or MRI scan to aid in the improvement of the surgeon’s decision-making and post-surgical outcome.
- AR-Based Medics: This refers to the use of AR in bringing real-life medics for training. They equip trainees and professionals with the means of applying procedure-related knowledge in immersive, hands-on exercises and get a vivid imagination of complex anatomical structures.
- AR Guidance Catheterization Systems: AR helps guide healthcare providers in catheterizing. Images and anatomical markers are superimposed over the patient’s body to make it more accurate and safer concerning fewer complications in catheter placement.
- AR for Surgeons in Glasses: Because such glasses will provide surgeons with patient information, imaging data, and instructional overlays right in their line of sight in the operating room, access to critical information they can view without needing to move their hands to access it augments concentration and reduces pulling attention away from the surgical site.

Breaking through the Hidden Barriers of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Challenge: High Cost of Implementation: The initial capital invested in AR technology and training would be too high, especially for the smaller medical facilities.
Solution: Flexibility in financing as well as partnering with the technology providers would lower the burden of the initial costs on them. Researching grants or subsidies to small medical facilities can make AR easier to implement.
Challenge: Technological Limitations: AR applications may result in hardware compatibility and high-quality imaging issues. This may limit its use severely and cause a delay in the effective delivery of practice.
Solution: Fund more research and development in compatible AR solutions for now’s hardware and with minimal imaging capabilities. The clinical effectiveness shall not be compromised. All this can be done in consultation with the manufacturers.
Challenge: Data Security and Privacy Issue: It is an unaddressed concern that the integration of AR in the healthcare segment would bring up a host of security issues related to the data stored about patients that need to be well-protected to avoid any breach of private information.
Solution: Advanced encryption methods and access control shall be established which will grant access to patient data only to selective users with regular audits and compliance checks to ensure the continuance of the standards of privacy and close identification on time.
Challenge: Resistance to Change: The healthcare provider is often averse to new technologies, especially if he is ignorant of AR or skeptical of its benefits.
Solution: Provide training that will enable a thorough understanding of how AR can be practically incorporated into the healthcare domain. Engage the early adapters as champions who can convince their peers and encourage innovation culture.
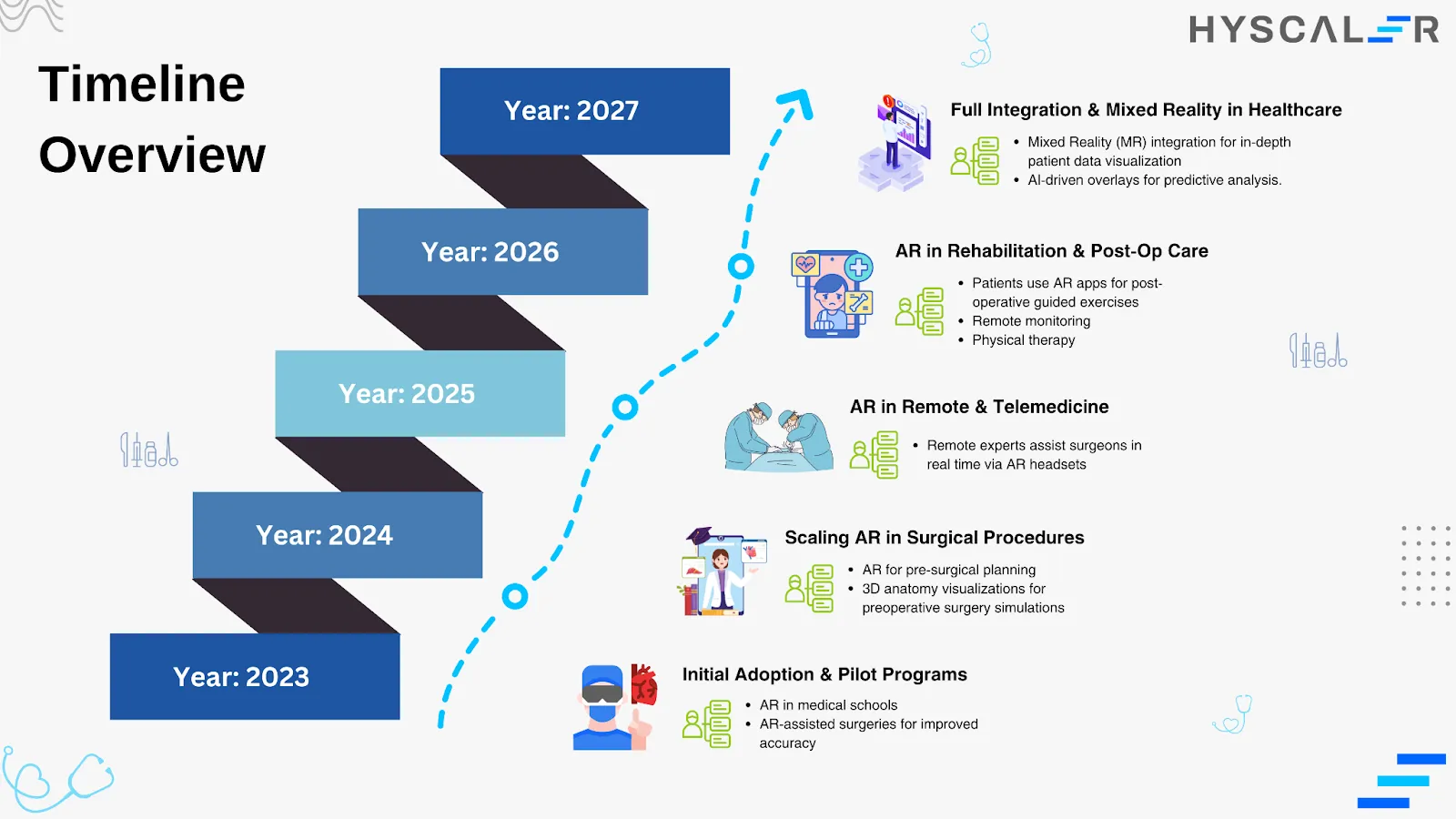
Augmented Reality’s Vision for Tomorrow in Healthcare
The future of augmented reality in healthcare promises to further enhance medical training, surgical precision, and patient engagement. As it keeps on evolving, AR will blend nicely with other digital health tools giving solutions to providers such as
- Improved hardware and more sophisticated software would enhance the accessibility of AR applications.
- Implementing better measures for the additional security of patient information is crucial.
- Innovations like mixed reality will provide more immersive experiences for both providers and patients.
- These advancements are expected to yield significantly enhanced outcomes in healthcare.
- Future developments will contribute to transforming healthcare, making it more efficient and patient-focused.
Curious about how these innovations can transform healthcare practices? Let’s explore the possibilities together and unlock the future of medical care.