Table of Contents
68% healthcare providers have adopted to the new technology
And, we are going to tell you why it’s important now? So read till the end.
Medical software development means creating apps and programs for healthcare. They help make healthcare easier, improve patient care, and lower costs.
Building medical software takes special skills. Developers know healthcare rules, understand patient needs, and keep updated with new technology.
Making medical software takes several steps: planning, designing, coding, testing, launching, and maintaining.
Medical software development is more than creating software.
It will help healthcare organizations to improve efficiency, and effectiveness in healthcare.
Software tools like management apps, telemedicine, and patient portals are important for healthcare.
We will explain key points for medical groups, software companies, startups, and medical device makers.
Now let’s dive in….
Who Require Healthcare Software Development?
Medical software development is not limited to any particular group or sector.
Here are some key groups that may need medical software development:
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals and clinics use medical software to keep patient records, set appointments, and manage billing. This software helps streamline operations, improve patient care, and enhance efficiency.
- Medical Device Manufacturers:Medical device makers often need custom software to make sure their products work well.
This software can control devices, collect and analyze data, and assist in diagnosing and treating patients. - Pharmaceutical Companies: Pharmaceutical companies use medical software for a variety of purposes, such as managing clinical trials, tracking drug interactions, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- Health Insurance Companies: Health insurance companies require medical software to manage policyholder information, process claims, and conduct risk analysis.
The software helps them provide better service to their customers and make more informed decisions. - Government Health Agencies: Government health agencies use medical software to monitor public health trends, manage healthcare programs, and maintain health records.
The software helps them make data-driven decisions and improve public health outcomes. - Patients: Patients also benefit from medical software. With the advent of telemedicine and health-tracking apps, patients can now monitor their health, schedule appointments, and communicate with their healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes.
Healthcare software development is crucial for various stakeholders in the healthcare industry.
It helps improve healthcare delivery, enhance patient care, and streamline operations.
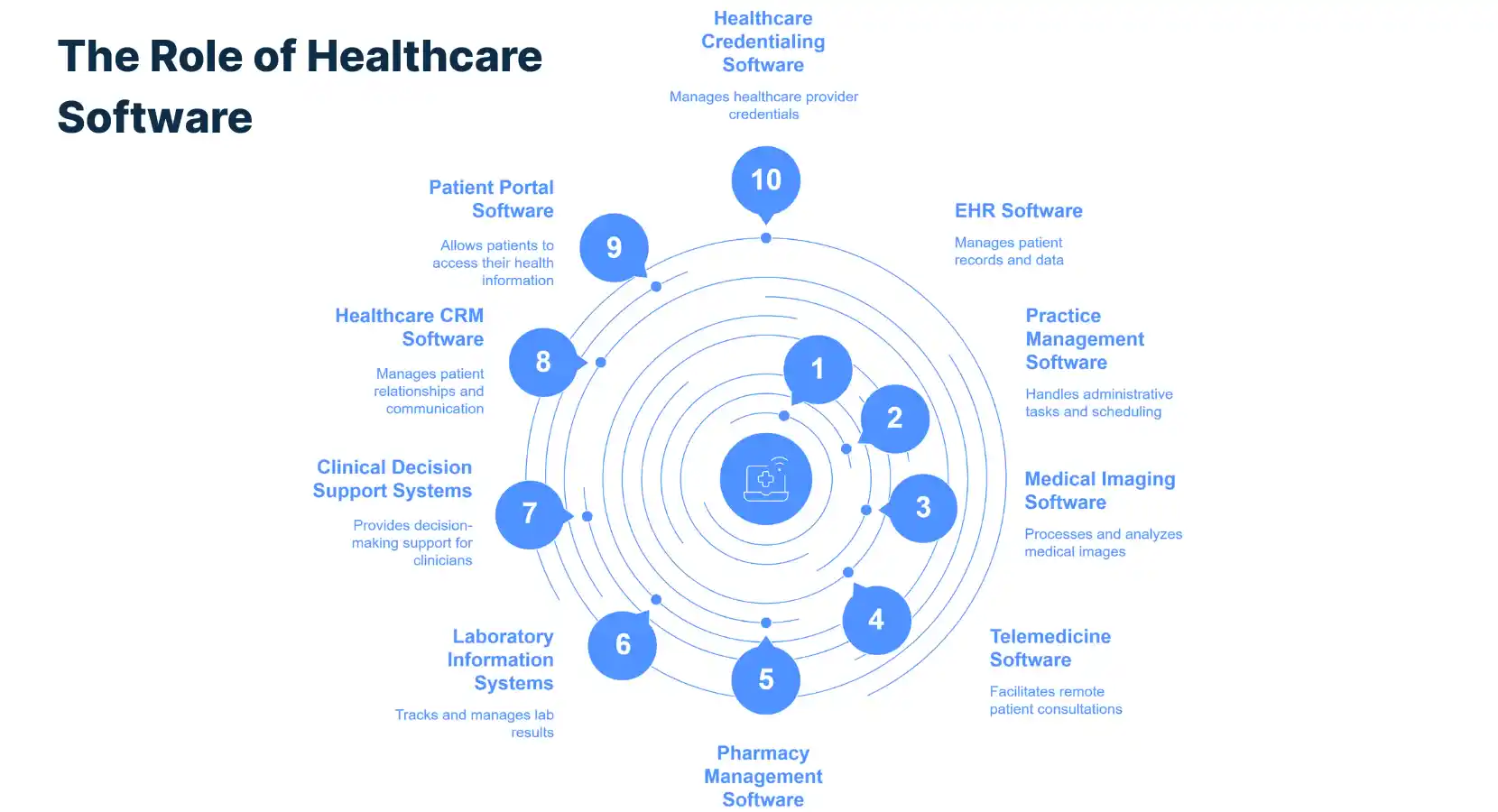
Different Types of Software for the Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry is a complex ecosystem with a wide range of software applications designed to streamline operations, improve patient care, and enhance medical research.
Here are some of the different types of software that are commonly used in the healthcare industry:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software: This type of software is used to store, retrieve, and manage patient health information digitally.
EHR software can include patient demographics, medical history, test and laboratory results, and even billing information.
It allows for seamless information sharing among healthcare providers, resulting in improved patient care. - Practice Management Software: This software helps healthcare providers manage the day-to-day operations of their practice.
The healthcare industry is a complex ecosystem with a wide range of software applications designed to streamline operations, improve patient care, and enhance medical research.
One such essential tool is a practice management system, which helps healthcare providers manage the day-to-day operations of their practice.
Here are some of the different types of software that are commonly used in the healthcare industry:
includes features for scheduling appointments, billing, reporting, and managing patient records. - Medical Imaging Software: This software is used to store and manage medical images such as X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasound images. It often includes tools for viewing, analyzing, and interpreting these images.
- Telemedicine Software: With the rise of digital health, telemedicine software has become increasingly important. This software enables healthcare providers to consult with patients remotely, offering convenience for both parties.
- Pharmacy Management Software: This software is used by pharmacies to manage the dispensing of medication, inventory management, and billing. It can also assist in achieving regulatory compliance.
- Laboratory Information Systems (LIS): LIS are computerized systems used in clinical laboratories for managing patient data, tracking test results, and automating workflows.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): These systems provide healthcare professionals with patient-specific assessments or recommendations to aid clinical decision-making.
- Healthcare CRM Software: This software helps healthcare organizations manage relationships with their patients and streamline processes related to marketing, sales, and customer service.
- Patient Portal Software: This software provides patients with secure access to their health data, including EHRs, test results, and doctor’s notes.
It often includes features for scheduling appointments, paying bills, and communicating with healthcare providers. - Healthcare Credentialing Software: This software helps healthcare organizations track, verify, and manage staff credentials, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
By automating credentialing tasks, healthcare credentialing software reduces administrative burden, improves accuracy, and ensures that only qualified personnel deliver patient care.
Each of these types of software plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, helping to improve efficiency, patient care, and overall operations.
The choice of software depends on the specific needs and requirements of the healthcare organization.
Custom Healthcare Software Development
Building medical software is complex and needs a good understanding of healthcare’s special needs and rules.
This section explains how to build custom medical software.
It covers the main steps in healthcare software development, and the best technologies to use for medical device software.
How To Know The Healthcare Software Development Process?
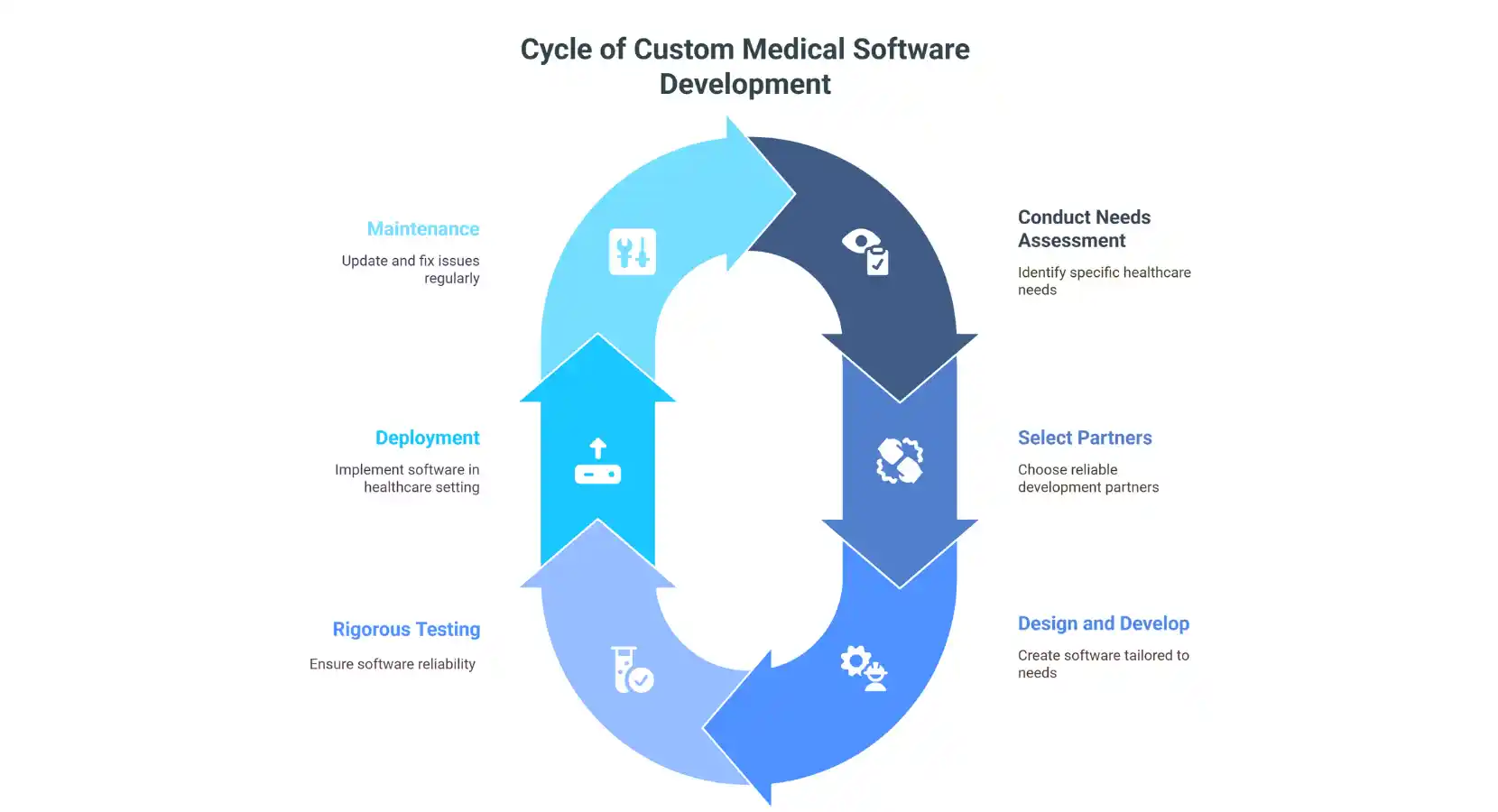
Building custom medical software takes several steps to make sure the final product meets the healthcare organization’s needs.
Here are the steps involved:
- Needs Assessment: This initial stage focuses on identifying your organization’s challenges and goals.
This includes listing the needed features, the problems you want to fix, and the results you hope to achieve. - Partner Selection: Choosing a trusted software partner with healthcare experience is very important.
Look for a team that understands the regulatory landscape and can translate your needs into a secure and compliant solution. - Design and Development: With clear requirements established, the development phase begins.
This includes creating an easy-to-use interface, setting up the backend, and adding the features you planned. - Rigorous Testing: After development, the software is tested to make sure it works as expected and has no errors.
This phase safeguards the quality and reliability of the software. - Deployment and Maintenance: After testing, the software is set up for use in your organization.
Regular maintenance is important to keep it running well and fix any future problems.
By following these steps, you can create high-quality healthcare software that meets your organization’s needs and improves patient care.
Tech Stack to Use in Medical Device Software Development
The technology stack used in medical device software development can vary depending on the specific needs of the project.
The tech stack play a major role in developing a healthcare software.
And, depending on the needs you need to use a different tech.
Here are some commonly used technologies in healthcare software development:
- Programming Languages: Java, Python, and C# are popular languages used in medical software development.
- Database Management Systems: MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB are popular choices for managing data.
- Frontend Technologies: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and various JavaScript frameworks such as Vue.Js, React, and TypeScript are typically used for front-end development.
- Backend Technologies: Node.js, Django, and .NET are commonly used for backend development.
- Mobile Development Platforms: For mobile applications, Android and iOS are the most commonly used platforms.
Remember, the choice of technology depends on your project’s needs and your development team’s skills.
Healthcare Software We Develop
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, it’s crucial to have software solutions that are tailored to meet the unique needs of various stakeholders.
We develop a wide range of healthcare software for different organizations and companies.
Our healthcare software development services span across:
For Healthcare Organizations, Software Product Companies, and Innovative Startups
Healthcare organizations, software product companies, and innovative startups have their own unique set of challenges and requirements.
We understand these needs and build software solutions that are tailored to their specific needs.
From Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems to hospital Management Systems (HMS), to patient engagement platforms, we have a broad portfolio that caters to these entities.
We also work with startups to develop innovative solutions that disrupt the healthcare industry, offering them the technological backbone they need to bring their ideas to life.
For billing companies aiming to optimize revenue, incorporating medical billing software for billing companies is pivotal.
This special software makes billing easier, improves accuracy in claims, and helps medical practices get paid faster.
For Medical Device Manufacturers and SaMD Companies
Medical device makers and SaMD companies lead the way in healthcare innovation.
We build strong software that helps them design, develop, and manage their products. Our software follows safety rules, is secure, and easy to use.
We also help build SaMD to make sure it’s safe, works well, and meets all required standards.
For Pharmaceutical, Biotech, and Life Science Companies
Pharma, biotech, and life science companies need specialized software solutions to manage their complex work and research. We create tools that support drug discovery, clinical trials, biotech research, and more. Our software helps teams work faster, manage data better, and boost research.
We also make sure our software meets all industry rules to keep quality and safety high.
Our healthcare software skills cover many parts of the industry. We focus on building custom, reliable, and safe solutions that help our clients reach their goals and improve healthcare.
Healthcare Software Development Costs and Timelines
The cost of developing healthcare software is a significant factor for many organizations.
It’s important to know that costs can vary a lot based on things like project complexity, the tech used, team size, and how long it takes to finish.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Complexity: The complexity of the software is the primary factor that influences the cost. Simple apps with basic features cost less than complex software with advanced tools.
For example, a basic appointment app costs much less than a full EHR system that works with other tools and devices. - Technology: The technology stack you choose will impact the cost.
Advanced tools like AI and ML help software run better and faster, but they also add to the cost of development. - Team Size: The size of the development team is another factor that impacts the cost.
A bigger team with different skills can build software faster and better, but it will also cost more. - Timeline: The timeline for the project also influences the cost. A shorter timeline will require more resources and therefore increase the cost.
- Estimated Cost: Because of these factors, it’s hard to give an exact estimate without knowing the details of the project.
As a rough estimate, a basic healthcare app might cost around $20,000, while a complex EHR system could start at $200,000. - Development Timelines: The timeline for developing healthcare software also varies widely. A basic app might take a few weeks to develop, while a complex EHR system could take several months or over a year.
The timeline depends on factors like the software’s complexity, the team size, and how efficient the development process is.
Understanding the factors that affect cost and timeline can help organizations plan and budget better.
It’s important to work with a trusted healthcare software development company that can provide a clear estimate based on your needs and goals, including regulatory compliance.
The development of medical software is a complex process that requires strict adherence to regulatory compliance.
Why is Regulatory Compliance Important?
Regulatory compliance isn’t a legal rule— it’s key to developing safe, effective, and high-quality medical software.
Failure to comply can lead to heavy fines, lawsuits, and harm to the company’s reputation.
Several regulatory bodies oversee the development and implementation of medical software worldwide. These include:
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA regulates medical devices, including software, in the U.S. Their guidelines for software validation are crucial for healthcare software developers.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA): The EMA regulates medical devices and software in the European Union. It provides guidelines on the development and validation of medical software.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): ISO 13485 is a standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices, including software.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA sets the rules for protecting sensitive patient information.
Any company handling protected health information (PHI) must ensure they have the right physical, network, and process security measures in place.
Compliance in the Development Process
Compliance should be an integral part of every stage of the medical software development process.
This includes:
- Design: The software should be designed to meet the specific regulatory requirements. This includes ensuring that the software is safe and effective and that it meets the needs of its intended users.
- Development: During development, the software should be tested and validated to make sure it meets regulatory standards. This includes conducting risk assessments and usability testing.
- Implementation: Once the software is developed, it should be implemented in a way that complies with the regulatory requirements.
This includes ensuring that the software is used correctly and that it is maintained and updated as necessary. - Post-market surveillance: After the software is on the market, it should be monitored to ensure it continues to comply with the regulations.
This includes reporting any adverse events and making any necessary updates or corrections.
Regulatory compliance is a fundamental aspect of medical software development.
It ensures that the software is safe, effective, and of high quality, thereby protecting the health and well-being of patients.
Healthcare Can Benefit From Medical Device Software Development
The growth of medical device software has transformed the healthcare industry, providing many benefits to healthcare businesses.
These benefits range from enhanced patient care to improved operational efficiency.
Here are some key benefits that medical device software development brings to healthcare businesses:
Improved Patient Care
Medical device software development has significantly improved the quality of patient care.
With software-enabled medical devices, healthcare providers can track patient health in real time, resulting in quicker diagnoses and treatments.
These devices can also create personalized care plans based on a patient’s unique health data, improving outcomes.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Medical software makes healthcare operations more efficient.
For example, it can automate tasks like scheduling appointments, billing, and managing patient records. This allows healthcare professionals to spend more time on patient care.
It also helps healthcare teams communicate and work together better, leading to quicker decisions and better coordination.
Cost Savings
Medical software can reduce healthcare costs by automating routine tasks and streamlining operations.
With real-time patient monitoring, experts can detect health issues and reduce hospital cost.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Medical device software can collect and analyze large amounts of health data by giving experts correct insights.
These insights helps in diagnosing diseases to creating treatment plans, and efficient care.
Improved Compliance
Medical device software can also help healthcare businesses follow regulatory requirements. For example, the software can automatically update patient records to keep them accurate and current.
Software can also provide audit trails which make it easier for healthcare to prove compliance during audits.
Increased Accessibility
Medical device software can also increase accessibility to healthcare services. For example, telemedicine software for mental health allows patients to consult with experts from home
In conclusion, medical device software development provides many benefits to healthcare businesses, making it a key part of modern healthcare.
By adopting this technology, healthcare businesses can improve patient care, boost efficiency, lower costs, make better decisions, ensure compliance, and increase access to healthcare services.
Medical Software Development Trends
The healthcare industry is constantly changing, with new medical technologies advancing quickly.
The realm of medical software development is no exception.
Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of this sector:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are changing the healthcare industry. These technologies are to analyze patient data, predict disease outbreaks, and make diagnoses.
In medical software development, AI and ML helps to create smart systems and make predictions or decisions.
2. Telemedicine: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine. Medical software development is now focused on telemedicine platforms.
Which help the patients to connect remotely with the doctor from any location.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare: IoT devices are used for remote patient monitoring, tracking health data, and offering personalized care.
IoT devices are used for remote patient monitoring, track their health and suggest treatment.
These devices ensure smooth data flow between devices and providers.
4. Blockchain in Healthcare: Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to ensure data security and privacy in healthcare.
Medical software developers are working on solutions that can leverage blockchain for the secure transfer of patient data, managing consent, and ensuring data integrity.
5. Big Data Analytics: Big data analytics is another trend shaping medical software development. It is being used for predictive analytics, population health management, and clinical decision support.
Medical software developers are creating solutions that can handle large volumes of data and provide actionable insights to healthcare providers.

6. Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud technology is being widely adopted in healthcare due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to facilitate real-time data sharing. Medical software development is moving towards creating cloud-based solutions that can be accessed from anywhere and at any time.
7. AR and VR Applications: AR and VR are being used for medical training, patient education, and therapeutic applications.
The development of medical software is being influenced by these technologies, with developers creating immersive and interactive applications for healthcare.
As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovation in this field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medical software development is a key part of modern healthcare. It brings many benefits, such as better patient care, easier admin work, and support for research and development.
Creating healthcare software is not easy. It needs a strong understanding of healthcare, solid technical skills, and careful attention to rules and standards. It’s not just about writing code—it’s about building tools that improve care quality.
Each healthcare group has different needs. That’s why custom software is important.
It ensures the software fits the group’s needs and follows the right rules.
The cost and time to build healthcare software can vary. It depends on how complex the project is, the tech used, and what the group needs.
That’s why it’s important to work with a skilled and trustworthy healthcare software development company.
The future of medical software looks bright.
New trends and tech are always appearing. Healthcare groups need to stay current to get the most from their software.
Lastly, medical software needs regular updates and care. This helps keep it working well and following the rules. It’s a long-term investment that brings great value to healthcare organizations.
In this fast-changing field, medical software will keep playing a big role. It’s a valuable effort that can raise the level of care and push the medical field forward.
FAQs
This section will answer some of the most frequently asked questions about healthcare software services.
Q1: What are healthcare software development services?
Software development for healthcare involves creating specialized software solutions for the healthcare sector. These solutions can include patient management systems, electronic health records, telemedicine apps, and complex medical imaging software.
Q2: What are the benefits of custom healthcare software development?
Custom healthcare software solutions development allows organizations to create solutions tailored to their specific needs. This can lead to improved efficiency, better patient care, and increased profitability.
Q3: How much does healthcare software development cost?
The cost of medical software development can vary widely depending on the complexity of the project, the technology used, and the development team’s location and expertise. It’s best to contact a healthcare software development company for a detailed quote.
Q4: What is the timeline for healthcare software development?
The timeline for healthcare software development can range from a few weeks to several months or even years. This depends on the complexity of the project, the development methodology used, and the resources available.
Q5: What are the regulatory compliance requirements for healthcare software?
Healthcare software must comply with a variety of regulations, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations for medical devices. These regulations ensure the privacy and security of patient data and the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
Q6: What are the latest trends in healthcare software development?
Current trends in custom healthcare software development solutions include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for predictive analytics, the rise of telemedicine, and the increased use of cloud-based solutions.
Q7: Can healthcare software be developed for mobile devices?
Yes, healthcare software can be developed for mobile devices. This includes applications for patient management, telemedicine, and remote patient monitoring.
Q8: How can healthcare software improve patient care?
Healthcare software can improve patient care by providing healthcare professionals with quick and easy access to patient records, improving communication between healthcare providers, enabling remote patient monitoring, and facilitating telemedicine services.
Q9: What is the role of security in healthcare software development?
Security is a critical component of custom healthcare software development services. Healthcare data is extremely sensitive, and breaches can result in serious consequences. Therefore, healthcare software must be developed with robust security measures in place to protect patient data.