Table of Contents
In the current fast-paced digital era, companies are always on the lookout for means to improve efficiency, minimize operational expenses, and enhance customer experiences. One technology that is transforming industries is Intelligent Automation (IA). Intelligent Automation integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) with automation technologies to develop self-learning and self-enhancing systems. It allows companies to automate intricate processes, make instant decisions, and improve overall productivity.
What is Intelligent Automation?
Intelligent Automation is the fusion of AI-based decision-making and automation technologies. While conventional automation executes actions according to predetermined rules, IA applies machine learning, cognitive computing, and robotic process automation (RPA) to interpret data, make decisions, and refine processes continually.
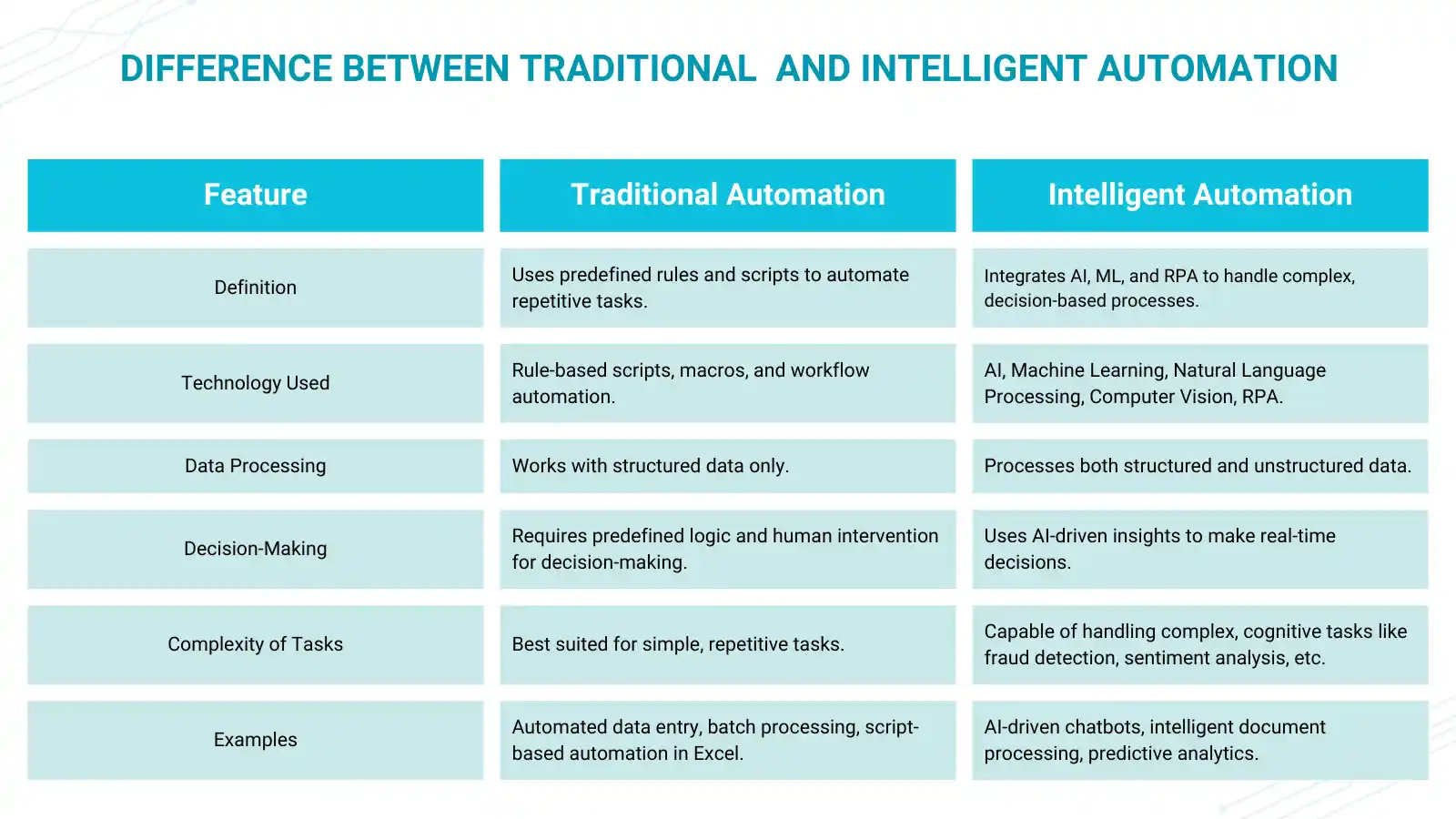
Difference Between Traditional Automation and Intelligent Automation
- Traditional Automation: Rule-based scripts, non-adaptive, and needs human interaction for decision-making in complex conditions.
- Intelligent Automation: Leverages AI and ML to learn from data, adjusts to new situations, and needs little or no human intervention.
How Intelligent Automation Works
The functionality of IA involves several key steps:
1. Data Collection
The basis of Intelligent Automation is the capacity to collect and process enormous volumes of data from various sources. This data may be structured, e.g., databases and spreadsheets, or unstructured, e.g., emails, social media messages, and multimedia. Sophisticated technologies utilized in this stage include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows systems to comprehend and interpret human language, making it possible to extract useful information from text data.
- Computer Vision: Enables computers to understand and process visual data, including images and videos, allowing for activities like image recognition and analysis.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Translates various types of documents, including scanned paper documents and PDFs, to editable and searchable information.
For example, in the health care industry, IA systems can read patient data from handwritten medical reports with the help of OCR and NLP and digitize the data for easier processing and analysis. This functionality not only saves time in manual data entry but also eliminates the errors involved in manual processing.
2. Analysis and Decision-Making
After data has been gathered, the subsequent step is to analyze this data in order to extract useful insights. Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are instrumental in this process by:
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: ML models are able to identify anomalies, forecast future occurrences, and identify patterns in big data.
- Making Informed Decisions: From the analysis, IA systems can be used to make decisions or offer suggestions, augmenting business processes’ speed and accuracy.
An example of practical application is in the financial sector, where IA systems review transaction information to identify fraudulent activity. By identifying suspicious patterns that do not follow a user’s normal behavior, the system is able to highlight possible fraud in real-time so that intervention can occur immediately.
3. Automation Execution
Following analysis and decision-making, the execution phase entails automating the required actions. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) steps in here by:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks: RPA bots can do repetitive tasks like data entry, processing invoices, and generating reports independently.
- Integrating with Existing Systems: These robots can communicate with different software programs, databases, and tools, allowing for smooth workflow integration.
For instance, in supply chain management, IA can process orders automatically. When a company receives an order, the system can automatically check inventory levels, process the order, update records, and start shipping—all automatically. This automates processing and increases accuracy.
4. Continuous Learning
A key characteristic of Intelligent Automation is its ability for ongoing learning and enhancement. With Machine Learning and feedback loops, IA systems can:
- Adapt to New Data: The more data is processed, the more the system adjusts its algorithms, becoming more accurate and efficient with time.
- Enhance Decision-Making Processes: Continuous learning allows the system to revise its decision-making factors based on emerging patterns and understanding.
In customer support, for example, chatbots that use IA learn with every interaction and improve their capability to solve issues effectively. They can address an increasing number of questions, respond more accurately, and refer a case to a human agent only when absolutely required.
Key Components of IA
Intelligent Automation (IA) represents the convergence of multiple advanced technologies designed to streamline and enhance business processes. By integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, and Process Mining, IA enables organizations to automate complex tasks, improve decision-making, and increase operational efficiency.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are the foundations of IA, giving systems the ability to read large sets of data, spot patterns, and make smart choices. AI covers a variety of technologies that imitate human thinking, such as problem-solving and learning. ML is a form of AI where algorithms learn through data to increase their performance as time passes without being programmed to do so.
Real-World Application:
In the financial industry, ML and AI are used to identify fraudulent transactions. Through the pattern analysis of transactions, these technologies can detect anomalies that signal fraud, allowing institutions to act promptly and reduce probable losses. For example, AI-based systems can track real-time transactions and report suspicious transactions for investigation.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is the application of software robots or “bots” to automate rule-based, repetitive tasks that were previously done by humans. These tasks include data entry, invoice processing, customer onboarding, and monitoring systems like a heat pump system. RPA increases efficiency, minimizes errors, and enables human employees to concentrate on more strategic tasks.
Real-World Application:
In the insurance sector, RPA is used to automate the process of claims. Bots are able to pull the information that is relevant from claim forms, check information against policy information, and make payments without any human intervention. This automation speeds up the claim process, reduces errors, and increases customer satisfaction.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows computers to comprehend, analyze, and create human language. NLP is critical for applications that involve human-computer interaction, including chatbots, virtual assistants, and sentiment analysis software. NLP enables systems to process unstructured data, such as text and speech, making communication more natural and efficient.
Real-World Application:
NLP-driven chatbots are used in customer service units to manage requests. The chatbots are capable of understanding customers’ questions, offering appropriate feedback, and taking serious issues forward to human assistants if needed. The application of NLP doesn’t just optimize response times but also guarantees continuous and accurate data transmission.
4. Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows machines to understand and process visual data from the world, like images and videos. It is essential for visual analysis-based tasks like quality inspection, face recognition, and medical imaging. Through visual data analysis, Computer Vision systems can detect objects, recognize anomalies, and enable automated decision-making.
Real-World Application:
Computer Vision is utilized for quality checking in manufacturing. Products on an assembly line are checked by cameras and image processing algorithms installed on the systems to identify defects and let only items that are within the quality threshold pass through. Automation minimizes manual checks and maximizes the consistency of the products.
5. Process Mining & Data Analytics
Process Mining is the study of business processes from event logs to determine inefficiencies and potential areas of improvement. Data Analytics is the study of datasets to make conclusions and inform decision-making. Combined, these elements reveal workflow efficiencies that allow organizations to streamline operations and improve performance.
Real-World Application:
In medicine, Data Analytics and Process Mining are utilized in patient care processes. Using data on treatment processes and patient records, bottlenecks, waiting times can be determined and the overall quality of care increased. For instance, comparing patient flow in departments can provide evidence of delay and guide changes to processes in order to optimize efficiency.
Use cases of Intelligent Automation by Industry
- Healthcare: At Chi Mei Medical Center in Taiwan, a software robot was developed to automatically download electronic invoice data and detect inconsistencies, significantly reducing manual auditing efforts.
- Manufacturing: Tesla’s introduction of the humanoid robot, Optimus, aims to address worker shortages and skill gaps by performing tasks traditionally handled by humans, thereby enhancing automation in manufacturing processes.
- Finance: Financial institutions employ AI-driven systems for fraud detection by analyzing transaction patterns to identify anomalies, thereby safeguarding against fraudulent activities.
- Retail and E-commerce: Companies like Amazon utilize AI-powered recommendation engines to analyze customer behavior and suggest products, enhancing the shopping experience and increasing sales.
- Human Resources: Organizations are adopting AI-driven chatbots to streamline recruitment by screening resumes and scheduling interviews, reducing the time and effort required in the hiring process.
Intelligent Automation in Big Tech
Many big tech organizations are leveraging Intelligent Automation (IA), which integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Business Process Management (BPM) to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve decision-making.
- Google has invested over $3.9 billion in AI research and development. It uses Google Cloud AI, TensorFlow, and Vertex AI for intelligent automation in applications such as Google Assistant, Google Ads, and YouTube content moderation. Additionally, its AI-driven automation in data centers has led to a 40% reduction in cooling energy usage.
- Microsoft integrates IA through Power Automate, Azure AI, and Dynamics 365. Microsoft 365 Copilot uses generative AI to automate workflows, email management, and document creation. With AI-powered Azure Cognitive Services, Microsoft has improved enterprise automation, leading to an estimated 30% boost in productivity for businesses using its cloud solutions.
- Amazon deploys AWS AI & ML services, Amazon Lex, and SageMaker for automation in cloud computing and customer interactions. In fulfillment centers, Amazon’s robotic automation, powered by Kiva robots, has cut operational costs by 20% and improved delivery speed. AI-driven Just Walk Out technology in Amazon Go stores processes over 1,000 transactions per second without human intervention.
- Apple applies IA through Core ML, SiriKit, and Apple Neural Engine to enhance automation in Siri, iCloud, and device performance optimization. AI-driven automation in Apple Maps and customer support bots has reduced response time by 50% and improved navigation accuracy by 20%.
- IBM has invested over $6 billion in AI and automation research, primarily through IBM Watson, IBM Cloud Pak for Automation, and AIOps. Watson AI has been used to automate customer service, reducing resolution time by 40% in industries like healthcare and finance. IBM’s cognitive automation has improved IT operations efficiency by 25%.
- Tesla incorporates IA in Full Self-Driving (FSD), Dojo AI, and Optimus robots for factory automation. Tesla’s Giga factories utilize robotic automation, resulting in a 30% increase in production efficiency. Its AI-driven energy management in Powerwall and Solar solutions has optimized energy consumption, reducing grid dependency by 35%.
Conclusion
Intelligent Automation is revolutionizing sectors by combining AI, ML, RPA, NLP, Computer Vision, and Process Mining. Challenges notwithstanding, companies that deploy IA strategically will be one step ahead in terms of competitiveness. As technology advances, IA will fuel innovation, efficiency, and more informed decision-making in every industry.
In adopting IA, companies are not merely mechanizing tasks; they are defining the future of digital transformation.