Table of Contents
Cyber threats are evolving at a rapid pace. Traditional security methods, such as firewalls and rule-based detection systems, are no longer enough to stop advanced attacks. Cybercriminals continuously find new ways to bypass security measures, making it harder for organizations to protect sensitive data.
Machine learning is reshaping cybersecurity by improving how threats are detected and handled. By analyzing large datasets, machine learning can recognize unusual patterns, detect potential threats, and respond in real time. These systems learn from past incidents and become more effective over time. Companies and security professionals are increasingly using AI-driven cybersecurity tools to prevent data breaches, identity theft, and other cybercrimes.
This article explores how machine learning improves cybersecurity, the role of engineers in this field, and how businesses and individuals benefit from these advancements.
The Role of Machine Learning in Threat Detection
Cybercriminals constantly refine their techniques, making it difficult for traditional security tools to detect threats. Many existing security systems rely on predefined rules, meaning they can only recognize known attacks. This approach fails when hackers develop new tactics.
Machine learning takes a different approach. Instead of relying on fixed rules, it learns from vast amounts of security data. By analyzing patterns in network traffic, login attempts, and user behavior, AI-driven security tools can detect anomalies that may indicate an attack. These tools help cybersecurity professionals identify threats faster, reducing the chances of data breaches.
The development of machine learning-based cybersecurity tools requires experts with strong data skills. Among the different type of engineers, data engineers play a key role. They collect, clean, and structure vast datasets to train machine learning models. These engineers build data pipelines that allow cybersecurity systems to analyze real-time information, detect threats, and respond immediately. Their work ensures that machine learning models remain accurate and effective in identifying risks.
Automating Cybersecurity Responses with AI
Cyberattacks can spread within seconds, leaving security teams with little time to react. In many cases, detecting a threat is not enough—organizations need immediate action to prevent further damage. Traditional security systems often require human intervention, which can slow down response times.
Machine learning improves cybersecurity by automating responses. AI-driven security tools can recognize suspicious activity and take action before a human gets involved. For example, an AI-powered system can block unauthorized login attempts, isolate infected devices from a network, or flag potentially harmful emails before they reach users.
By automating responses, organizations reduce the chances of human error and minimize the impact of cyberattacks. Security teams can focus on analyzing complex threats while machine learning handles routine security measures. This approach allows businesses to strengthen their cybersecurity without increasing staff workload.
Predictive Analysis: Preventing Attacks Before They Happen
Machine learning is valuable for detecting active threats, but its ability to predict cyberattacks is just as important. Instead of waiting for an attack to occur, predictive models analyze historical data to identify patterns that indicate potential risks. These models use past security incidents, network activity, and user behaviors to assess vulnerabilities before cybercriminals exploit them.
Organizations benefit from predictive cybersecurity because it helps strengthen defenses before hackers find weaknesses. Businesses can identify outdated software, suspicious activity, or weak access controls that could lead to breaches. By using machine learning to evaluate risks, companies can take preventive steps, reducing the likelihood of costly cyber incidents.
Predictive models also help in fraud prevention. Financial institutions use AI to analyze transaction data and flag suspicious activity. If a transaction deviates from a user’s typical behavior, the system can block it and alert security teams. This approach reduces fraud-related losses and protects customers from identity theft.
Enhancing Identity Verification and Fraud Detection
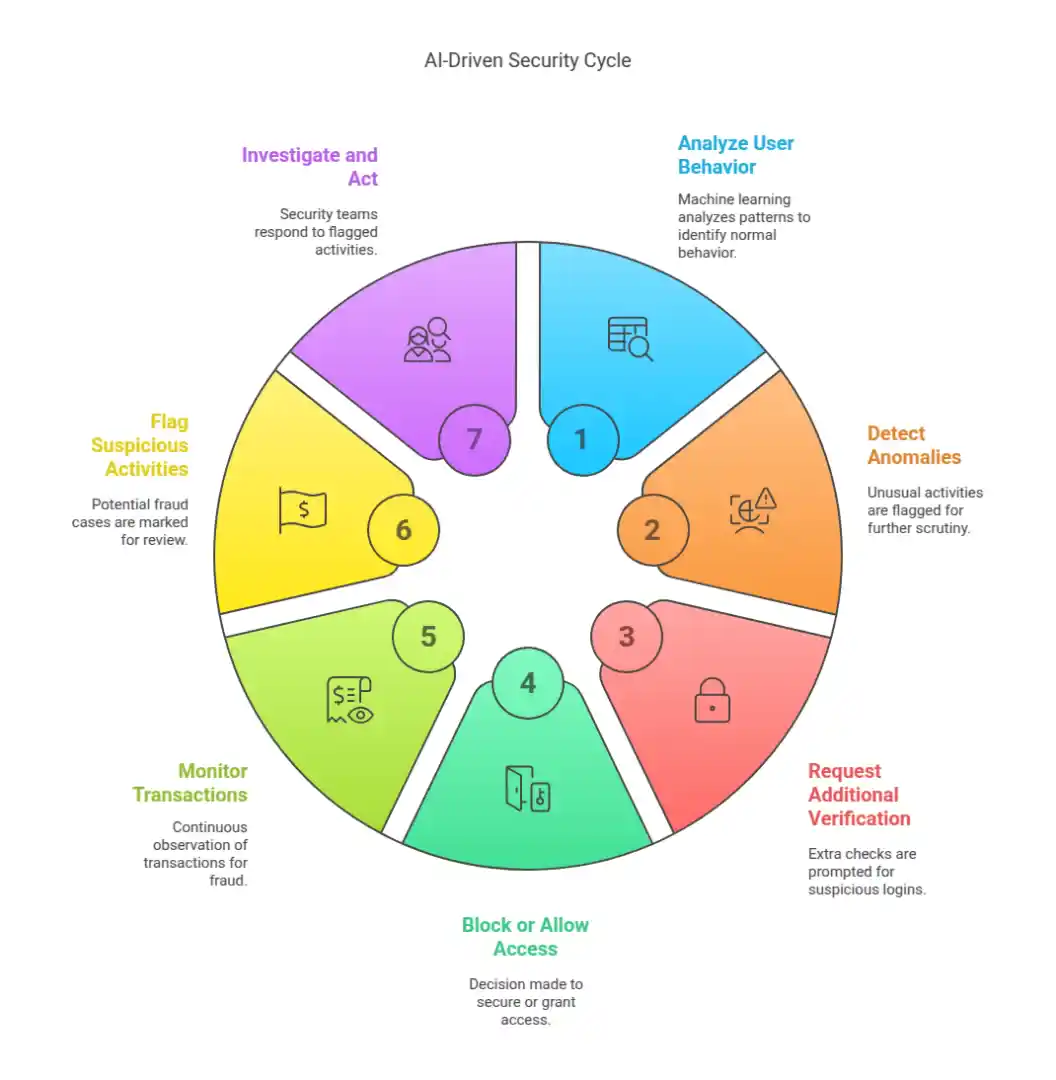
Cybercriminals frequently target login credentials, using stolen passwords to gain access to sensitive accounts. Traditional security methods, such as passwords and two-factor authentication, are not always enough to stop attackers. Machine learning improves identity verification by analyzing user behavior, biometric data, and access patterns.
AI-driven authentication systems detect unusual login attempts by evaluating factors like location, device type, and typing speed. If a login request comes from an unfamiliar location or shows suspicious behavior, the system can request additional verification or block access. These advanced security measures make it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized entry.
Machine learning is also transforming fraud detection. With AI fraud detection software, businesses can automate fraud prevention, making real-time security decisions based on behavioral patterns. Banks and online retailers use AI to analyze purchasing behaviors and detect potential fraud in real time. If an account suddenly makes multiple high-value purchases or attempts transactions from different locations within a short period, AI-driven systems can flag the activity. Security teams can then investigate and take appropriate action before financial damage occurs.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns in AI-Based Cybersecurity
Machine learning enhances cybersecurity, but it also presents challenges. Cybercriminals use AI to develop more sophisticated attacks, making security an ongoing battle. Hackers have created malware that learns how to evade detection, making traditional defense strategies less effective. Cybersecurity professionals must constantly update machine learning models to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Another challenge is bias in AI models. If a machine learning system is trained on biased data, it may overlook certain threats or flag harmless activities as risks. This issue can lead to false positives, where legitimate users are blocked, or false negatives, where actual threats go undetected. Engineers must carefully design models to reduce bias and improve accuracy.
Privacy concerns also arise when companies collect large amounts of user data for cybersecurity purposes. While AI-driven security tools improve protection, organizations must balance security with privacy rights. Users need clear guidelines on how their data is used, stored, and protected.
Machine learning is transforming cybersecurity by improving threat detection, automating responses, and predicting attacks before they happen. Organizations rely on AI to analyze large datasets, detect unusual patterns, and prevent security breaches. Data engineers and other professionals play a critical role in developing AI-driven security solutions, making machine learning an essential part of modern cybersecurity. As threats evolve, machine learning will continue to be a powerful tool in protecting businesses and individuals from cyber risks.